
Producing the required exterior polish for a processed workpiece is highly significant.
- CAD annotations convey exact surface criteria for production
- These callouts often use terms like "Ra," which stands for arithmetic mean deviation to quantify the surface roughness
- Appreciating callout details is key to ensuring product functionality
- Chosen finish influences lubrication retention, friction behavior, and part life
- Careful reading of finish callouts enables achieving the planned outcome
Precision Engineering Through CNC Machining
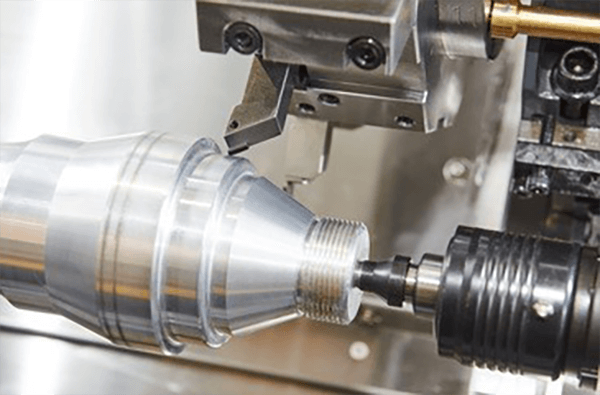
Automated machining signifies a significant manufacturing innovation via numerical control software the system carves sophisticated geometries with precision.
- This process enables the creation of high-quality parts from a wide range of materials
- Broad CNC applicability benefits industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare
- Machine-controlled machining secures stable repeatability for production lots
From small prototypes to large-volume runs CNC machining performs a central function in today's manufacturing landscape
Deciphering CNC Machine Specifications
Decoding CNC machine specifications can feel daunting at first glance
Nevertheless simple study and a stepwise method let you read technical specifications
Start with locating core parameters: spindle rpm, feed, accuracy, work envelope, controller
Every listed attribute influences the equipment’s operational capacity.
To illustrate, faster spindle rotation fits soft materials and quicker feed improves production rates.
Appreciating such links enables selection of equipment fit for your objectives
Ensure you peruse vendor documentation exhaustively.
Those resources usually offer helpful explanations and clarify jargon
What is a CNC Machine? A Comprehensive Guide
Programmed machining equipment comprises computer-managed tools for exact automated fabrication of diverse materials They process programmed G-code to regulate toolpaths and actuator behavior.
- Frequent CNC varieties include mills, lathes, routers, plasma cutting machines
- Cutting methods suit steels, plastics, woods, and layered composites
- Additionally CNC gear supports fast prototyping and limited production for entrepreneurs and institutes
Core Concepts of CNC Machinery
They demonstrate convergence of tight hardware tolerances and refined software control These versatile tools utilize computer programming to automatically manufacture a wide range of parts from simple components to complex assemblies Underlying principle converts virtual designs into actual manufactured items.
- Numerical control manufacturing
- Software-guided fabrication
It follows systematic positional moves controlled by code Engineers contribute by setting machining variables, overseeing runs, and assuring product standards.
Surface Finish's Importance in CNC Machining
Producing expected finish through machining is important It changes how a part performs and how it looks Material characteristics, tool parameters, and finishing techniques affect texture.
A polished finish improves wear resistance whereas coarse texture can hinder performance CNC machining processes offer a wide range of tools and techniques to achieve the specific surface finish for different applications.
- Including selection of alternative tool profiles |high-speed steels|cutting speeds to achieve a desired surface finish
- In addition buffing, grinding, and sanding may be applied to upgrade finishes
Seeing how process parameters map to surface output is key for optimal finishes.
Introduction to CNC Machining
It constitutes a high-precision manufacturing approach using programmed machine tools to form parts from many materials They follow G-code sequences to generate complex parts reliably A fundamental understanding of CNC machine operation including the role of G-code programming and tool selection is essential for successful machining processes
Industry applications include aircraft, automotive, medical, electronics, and beyond From engine components to precision tooling, CNC enables production of sophisticated geometries
How to Specify Surface Finish for CNC Parts
Exact finish callout is important for CNC component manufacturing It secures that the final item meets both functionality and looks Callouts commonly use the roughness average (Ra) system to denote surface finish Measured in micrometers or inches, the number reflects mean surface roughness height.
Account for desired texture and the component’s purpose when selecting finish

Example: polished finishes often suit parts needing close tolerances and exact mating
Rugged finishes sometimes serve parts that need enhanced traction or grip
Apply clear finish annotations in technical drawings to state desired texture Document the Ra value and enumerate any extra finishing or treatment instructions.
Keep in mind clear finish callouts are central to manufacturing success
Types of CNC Machines and Their Capabilities
Numerical control machining comprises numerous machine types engineered for diverse applications They leverage CAD/CAM designs to instruct cutters for accurate and efficient fabrication.
- Milling centers craft intricate contours cavities and surfaces by subtractive cutting
- Lathes excel at producing round parts such as shafts rods and bushings
- Waterjet cutters use high-pressure abrasive streams to cut diverse materials without thermal effects
Decision factors include the part’s material, feature complexity, and tolerance specifications Specialized CNC abilities fulfill industry requirements across sectors from transport to healthcare.
Reaching Optimal Surface Quality Using CNC
Attaining top-quality surfaces is critical in fabrication and CNC techniques facilitate that achievement Through tailored feed rates spindle selection and tool design engineers control surface formation and limit imperfections Moreover premium cutters and correct coolant application enhance surface outcomes Well-chosen cutting tactics plus careful setup empower manufacture of parts with exceptional surfaces.
Programming Strategies for Surface Finish
Skillful CNC programming directly impacts the final surface quality The chosen machining parameters including feed rate spindle speed and cutting tool geometry exert a significant influence on the final surface texture Deliberate parameter selection and optimized lubrication enable near-flawless finishes.
- Additionally routine tool checks and upkeep maintain consistent finish quality In addition periodic tool servicing and checks secure consistent surface quality what cnc Plus regular inspection and maintenance of tools copyright finishing standards
- To enhance finish consider workpiece material, roughness targets and use case
- Simulated machining supports parameter refinement to mitigate surface issues
- Plus regular inspection and maintenance of tools copyright finishing standards
